Burkina Faso: Jihadists Intensify Attacks on Security Forces in September 2023
October 8, 2023
Senegal: Postponed Elections & Looming Political Unrest
February 5, 2024CONAKRY MAIN FUEL DEPOT EXPLOSION: IMPACT ASSESSMENT & FORECAST
Overview of Incident
Event: Significant explosion at Conakry's primary fuel depot.
Date: December 19, 2023.
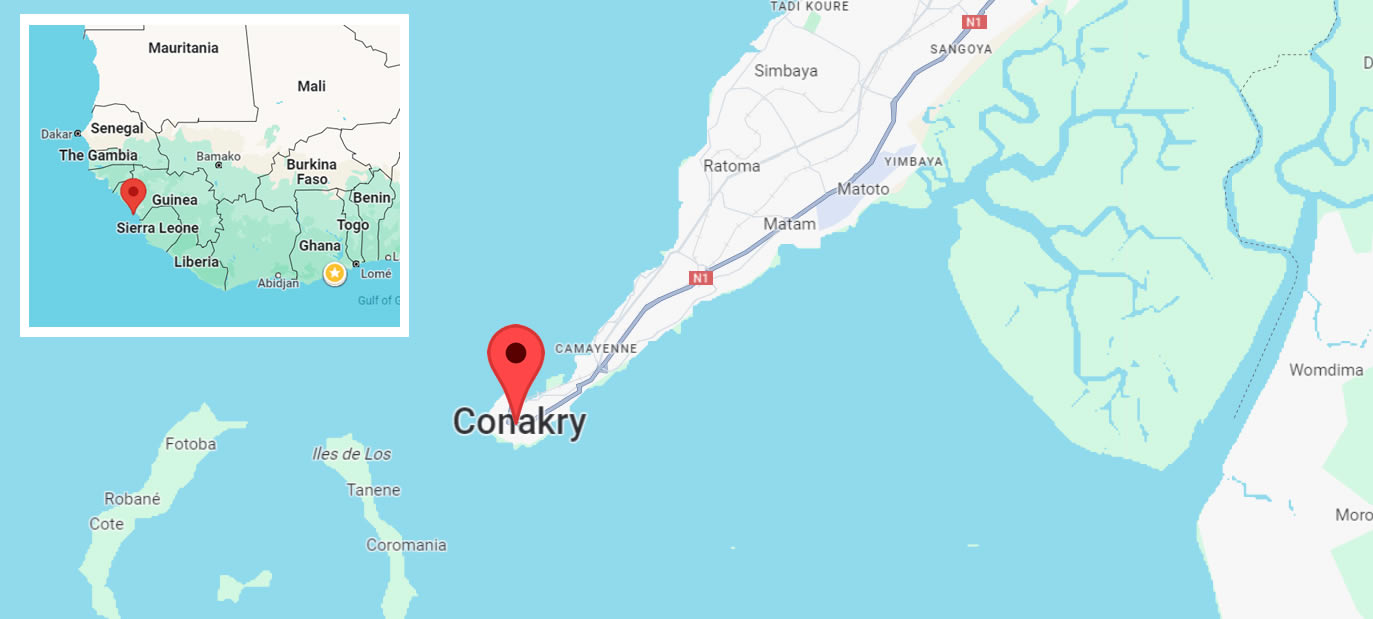
Location: Conakry, Guinea's capital.
Immediate Impact
Casualties: Approximately 18 fatalities and over 200 injuries.
Displacement: Significant, especially in the impoverished Coronthie area.
Property Damage: Major destruction of the central fuel depot, causing critical disruptions in fuel distribution.
Supply Chain Impact: Shutdown of key gas stations and tanker operations, leading to immediate fuel shortages.
Government Response
Emergency Actions: Launch of an investigation; closure of various public spaces and gas stations.
Relief Initiatives: Provision of temporary shelters for the displaced.
Infrastructure Monitoring: Advisory on potential electricity supply interruptions, yet no immediate major disruptions observed.
Location of the Explosion
Background
Energy Sector: Pre-incident, Guinea faced challenges in its energy sector, with frequent power outages indicating infrastructure weaknesses. The country relies heavily on imported petroleum, and the now-destroyed depot played a vital role in distribution. Guinea’s electrification rate stands at just around 46.8%, with a heavy reliance on fossil fuels (over 22% of the energy mix).
Economy: With an estimated real GDP of $35.729 billion in 2021, Guinea's economy is largely dependent on mining, particularly bauxite, and agriculture, making it vulnerable to external shocks.
Political Context: Post-2021 coup, Guinea is under a transitional government, grappling with challenges in governance and stability.
Security Situation: Pre-existing socio-economic issues often spark civil unrest. The country has seen a marginal decrease of 3.86% in security incidents but a notable increase of 20.34% in fatalities compared to the previous year, indicating escalating tensions.
Analysis
Energy Sector Vulnerability: The explosion has incapacitated a crucial node in Guinea's fuel supply chain, potentially leading to a spike in fuel prices and exacerbating the existing energy crisis.
Hoarding Concerns: There is an increased likelihood of fuel hoarding by other bulk storage facilities, which could worsen the fuel shortage and amplify price hikes.
Socio-economic Implications: The incident may deepen socio-economic disparities, especially among the lower-income groups directly affected by fuel shortages and increased transportation costs.
Political Stability Risk: The incident poses a significant challenge to the transitional government's ability to maintain stability and public trust, especially given the backdrop of heightened security incidents and fatalities.
Forecast
Energy Sector: Prolonged fuel shortages expected, with a potential increase in energy prices by over 150%, similar to recent crises. Recovery efforts could be hampered by the country's limited resources.
Economic Impact: Projected inflation spike could exceed the current 12% rate. Disruptions in transportation and business operations may lead to a GDP growth reduction by 2-3% in the short term.
Political Ramifications: Increased public dissatisfaction may lead to heightened protests and political unrest, potentially disrupting the transitional government’s efforts to stabilize the country.
Security Concerns: Elevated risk of civil unrest, with potential for violent confrontations between civilians and security forces. Regional stability might be impacted, with ECOWAS playing a critical role in maintaining order.